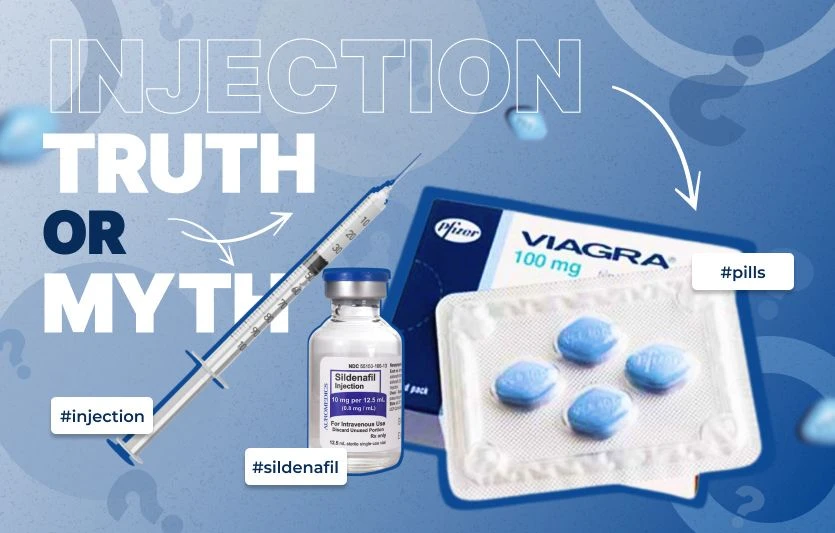
Generic name: sildenafil (oral) [sil-DEN-a-fil]
Brand names: Revatio, Viagra
Active ingredient: sildenafil
Drug class: Erectile dysfunction agents
Agency product number: EMEA/H/C/000202
International non-proprietary name (INN) or common name: sildenafil
Therapeutic area (MeSH): Erectile Dysfunction
Anatomical therapeutic chemical (ATC) code: G04BE03
Please read this leaflet carefully before you start using Viagra.
Viagra is a medicine used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED, also called erectile dysfunction). It is sometimes called sildenafil. It relaxes penile blood vessels, enabling blood to circulate and generating an erection. Take Viagra one hour before sexual activity.
You may achieve an erection for up to 4 hours after taking Viagra, but it won’t stay long.
Sexual excitement is still essential with Viagra. It doesn’t treat ED, boost sexual desire, prevent STDs, or act as male birth control. Viagra shouldn’t be used more than once per day or with other ED medications.
See TGA-approved patient labelling
Some medicines can cause unwanted or dangerous effects when used with Viagra. Tell your doctor about all your current medicines, especially riociguat (Adempas) and nitrates.
Do not take Viagra if you are also using a nitrate drug for chest pain or heart problems, including nitroglycerin, isosorbide dinitrate, isosorbide mononitrate, and some recreational drugs such as “poppers”. Taking sildenafil with nitrate medicine can cause a sudden and serious decrease in blood pressure.
Contact your doctor or seek emergency medical attention if your erection is painful or lasts longer than 4 hours. A prolonged erection (priapism) can damage the penis.
Stop using Viagra and get emergency medical help if you have sudden vision loss.
Yes, it does. In several clinical studies, Viagra was effective in treating ED. In these studies, men who used the drug had an improved ability to have and keep erections that allowed for successful sex.
Across the studies, between 43% and 83% of men who took Viagra had improved erections. (These rates varied depending on the cause of their ED and the dosage of Viagra being used.) In comparison, improved erections occurred in 10% to 24% of men who took a placebo (no active drug).
To learn more about Viagra’s effectiveness, see the “Viagra uses” section below.
Consult your doctor before using Viagra. Certain medical disorders or health issues may prevent you from taking the drug.
Medical condition | Explanation |
History of allergic reaction to Viagra or sildenafil. | Don’t take Viagra if you’ve ever had an allergic reaction to Viagra or sildenafil (the active drug in Viagra). If you’re not sure of your medication allergies, talk with your doctor. |
Heart problems or stroke. Heart problems include conditions such as angina (a type of chest pain), heart attack, heart failure, and aortic stenosis (narrowing of the main artery that leaves your heart). Heart problems also include irregular heartbeat patterns, such as atrial fibrillation (A-fib). | If you have a heart problem, or you’ve had a heart problem or stroke in the past, discuss Viagra’s safety with your doctor. Your doctor may not advocate Viagra and sexual activity if they would strain your heart. Stop sexual activity if you suffer chest pain, dizziness, or nausea while taking Viagra. While taking Viagra, don’t use nitrates for chest discomfort. If you develop life-threatening cardiac symptoms, call 000. Before using Viagra again, visit your doctor. |
High blood pressure | Viagra lowers BP. If you’re using blood pressure medicine, Viagra might lower it more. This might induce dizziness or fainting. Uncontrolled high blood pressure (over 170/110 mmHg) may not be good for sex. Consult your doctor if you have high blood pressure about Viagra. If you can take Viagra, your doctor will recommend a lesser dose. |
Low blood pressure | Viagra can lower your blood pressure. If you already have low blood pressure, Viagra lowers it further. This may induce dizziness or fainting. Consult your doctor if your blood pressure is below 90/50 mmHg. If you can take Viagra, your doctor will recommend a lesser dose. |
Physical abnormalities affecting your penis | Viagra may not be safe if you have a bending, scarring, or Peyronie’s disease.Peyronie’s illness causes penile curvature. Viagra causes priapism rarely (a long-lasting and sometimes painful erection). Priapism with Viagra might harm your penis if you have a physical condition. Discuss Viagra with your doctor. |
Blood cell problems | If you have a blood cell problem, such as sickle cell anemia, multiple myeloma, or leukemia, Viagra may not be safe for you.These disorders might raise your risk of priapism (a lengthy, painful erection) with Viagra. |
Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) | NAION causes optic nerve injury. This damages one or both eyes, causing abrupt visual loss. Viagra sometimes causes this. If you’ve experienced this eye disease before, Viagra may cause it. |
Hereditary retinitis pigmentosa | This eye disease is usually inherited. Viagra hasn’t been investigated in hRP. Eye problems? See your doctor. They’ll promote Viagra’s safety. |
Severe kidney problems | Viagra may build up if your kidneys don’t perform properly. This increases pharmacological side effects. Your doctor will prescribe a lesser dose of Viagra if you have serious renal issues. |
Liver problems | Viagra might build up if your liver isn’t working effectively. This increases pharmacological side effects. Your doctor will prescribe a lower dose of Viagra if you have liver issues. |
Bleeding problems | Since Viagra’s approval and distribution, a few users have reported bleeding. Viagra didn’t create these issues, however. Viagra’s safety for bleeding disorders is unknown. Consult your doctor if you have bleeding issues before using Viagra. |
Peptic ulcer | Viagra’s safety for people with a peptic ulcer isn’t well-studied. Consult your doctor if you have or had an ulcer about using Viagra. |
Pregnancy | Viagra isn’t approved for use in women. |
Breastfeeding | Viagra isn’t approved for use in women. |
Note: For more information about the potential negative effects of Viagra, see the “Viagra side effects” section above.
Sildenafil is used to treat male sexual function problems (erectile dysfunction or erectile dysfunction-ED). In combination with sexual stimulation, sildenafil works by increasing blood flow to the penis to help a man get and keep an erection. This drug does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases (such as HIV, hepatitis B, gonorrhea, syphilis). Practice “safe sex” such as using latex condoms. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for more details.
Read the Patient Information Leaflet provided by your pharmacist before you start taking sildenafil and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
To treat erectile dysfunction-ED, take this drug by mouth as directed by your doctor, usually as needed. Take sildenafil at least 30 minutes, but no more than 4 hours, before sexual activity (1 hour before is the most effective). Do not take more than once daily.
A high-fat meal may delay how quickly the drug begins to work.
The dosage is based on your medical condition, response to treatment, and other medications you may be taking. Be sure to tell your doctor and pharmacist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).
Tell your doctor if your condition does not improve
The Viagra dosage your doctor prescribes will depend on several factors. These include:
- your age
- whether you have liver or kidney problems
- other medical conditions you may have
- other medications you may be taking
The following information describes dosages that are commonly used or recommended. However, be sure to take the dosage your doctor prescribes for you. Your doctor will determine the best dosage to fit your needs.
The appropriate dosage of Viagra may vary between people. Your doctor will be able to determine the right dosage for you.
The number of doses taken daily depends on why Viagra is being used. Viagra is taken orally.
For use in erectile dysfunction:
- Adults ages up to 64 years old typically take 50 milligrams (mg) 1 hour before sexual intercourse, no more than once a day.
- For adults ages 65 and older using Viagra for erectile dysfunction, or for those with cirrhosis or severe renal impairment, the average dose is 25 mg as a single dose, taken 1 hour before sexual intercourse, but no more than once a day.
Viagra may also be taken between 30 minutes to 4 hours prior to sexual intercourse.
Your doctor may adjust your dosage to meet your needs.
Viagra may also be used for pulmonary arterial hypertension. When used for this purpose, the average dose is 5 to 20 mg of Viagra taken 3 times a day. The doses of Viagra should be taken between 4 to 6 hours apart when used for pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Age | Dosage | When to take |
| Adults ages up to 64 years old | 50 mg, no more than once a day | 1 hour prior to sexual intercourse (alternatively, may also be taken between 30 minutes and 4 hours prior to sexual intercourse) |
| Adults ages 65 and older, or with cirrhosis or severe renal impairment | 25 mg, no more than once a day | 1 hour prior to sexual intercourse (alternatively, may also be taken between 30 minutes and 4 hours prior to sexual intercourse) |
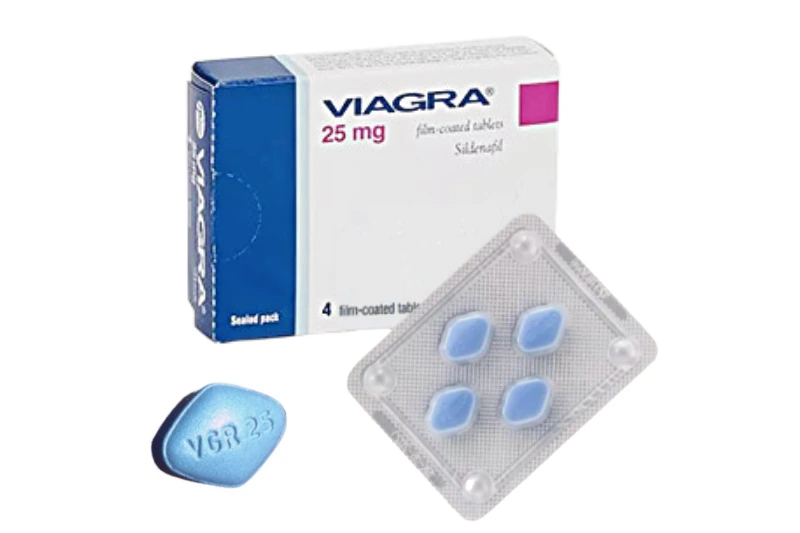
Viagra comes as tablets that are taken by mouth. It’s available in three strengths: 25 mg, 50 mg, and 100 mg.
Color: blue coloured diamond shaped film coated tablet
Color: blue coloured diamond shaped film coated tablet

Color: blue coloured diamond shaped film coated tablet
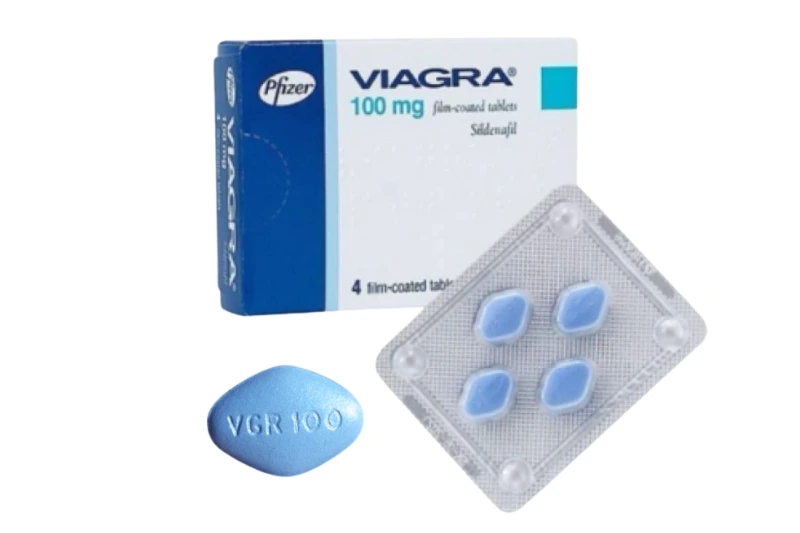
The typical dose of Viagra for erectile dysfunction (ED) is 50 mg. You can take this dose 30 minutes to 4 hours before you plan to have sexual activity. But for most people, it’s recommended that you take your dose about an hour before having sex. Don’t take Viagra more than once a day.
Your doctor may prescribe a different dosage of Viagra for you depending on several factors. These factors may include whether you have liver or kidney problems, or if you’re taking certain other medications. If any of these factors apply to you, your starting dose might be 25 mg, which is lower than the typical recommended dose.
If you have questions about the Viagra dosage that’s right for you, talk with your doctor.
And keep in mind that if Viagra isn’t working for you, your doctor may increase your dose of the drug. But the maximum dose of Viagra is 100 mg.
Since Viagra is used as needed, you are not likely to miss a dose.
Using more than the recommended dosage of Viagra can lead to serious side effects. Do not use more Viagra than your doctor recommends.
If you think you’ve taken too much of this drug, call your doctor. You can also call the American Association of Poison Control Centers at 800-222-1222 or use their online tool. But if your symptoms are severe, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room right away.
Viagra can interact with several other medications. Different interactions can cause different effects. For instance, some interactions can interfere with how well a drug works. Other interactions can increase side effects or make them more severe.
Below are lists of medications that can interact with Viagra. These lists don’t contain all the drugs that may interact with Viagra.
Before taking Viagra, talk with your doctor and pharmacist. Tell them about all prescriptions, over-the-counter, and other drugs you take. Also, tell them about any vitamins, herbs, and supplements you use. Sharing this information can help you avoid potential interactions.
If you have questions about drug interactions that may affect you, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
You shouldn’t take Viagra with any other medications for erectile dysfunction (ED). This includes prescription medications, such as:
- tadalafil (Cialis)
- avanafil (Stendra)
- vardenafil (Levitra, Staxyn)
- alprostadil (Muse, Caverject, Caverject Impulse, Edex)
It also includes natural or over-the-counter ED treatments, such as l-arginine and yohimbine.
Taking Viagra with other ED medications increases your risk of certain side effects, such as low blood pressure and priapism.*
If you’re using Viagra, don’t use any other medications for ED without talking with your doctor.
* Priapism is a long-lasting and sometimes painful erection that doesn’t go away. It’s a medical emergency because it can damage the tissues in your penis and lead to permanent ED.
Viagra can cause mild or serious side effects. The following lists contain some of the key side effects that may occur while taking Viagra. These lists don’t include all possible side effects.
For more information on the possible side effects of Viagra, talk with your doctor or pharmacist. They can give you tips on how to deal with any side effects that may be bothersome.
Note: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) tracks the side effects of drugs it has approved. If you would like to report to the FDA a side effect you’ve had with Viagra, you can do so through MedWatch.
Mild side effects | Serious side effects | Side effect details |
Most of these side effects may go away within a few days or a couple of weeks. But if they become more severe or don’t go away, talk with your doctor or pharmacist. * This is a partial list of mild side effects of Viagra. To learn about other mild side effects, talk with your doctor or pharmacist, or view the drug’s patient information. |
Other serious side effects, which are explained in more detail in “Side effect details,” include:
| Allergic reaction As with most drugs, some people can have an allergic reaction after taking Viagra. In clinical studies, less than 2% of people who took Viagra had an allergic reaction. It’s not known how often allergic reactions occurred in people who took a placebo (no active drug). Symptoms of a mild allergic reaction can include:
A more severe allergic reaction is rare but possible. Symptoms of a severe allergic reaction can include:
|
Call your doctor right away if you have a severe allergic reaction to Viagra. But call 000 if your symptoms feel life-threatening or if you think you have a medical emergency.
Adverse Reaction | 25 mg (n=312) | 50 mg (n=511) | 100 mg (n=506) | Placebo (n=607) |
| Headache | 16% | 21% | 28% | 7% |
| Flushing | 10% | 19% | 18% | 2% |
| Dyspepsia | 3% | 9% | 17% | 2% |
| Abnormal vision† | 1% | 2% | 11% | 1% |
| Nasal congestion | 4% | 4% | 9% | 2% |
| Back pain | 3% | 4% | 4% | 2% |
| Myalgia | 2% | 2% | 4% | 1% |
| Nausea | 2% | 3% | 3% | 1% |
| Dizziness | 3% | 4% | 3% | 2% |
| Rash | 1% | 2% | 3% | 1% |
| †Abnormal Vision: Mild to moderate in severity and transient, predominantly color tinge to vision, but also increased sensitivity to light, or blurred vision. | ||||
- Viagra 25mg film-coated tablets. Available from: [URL_Link]
- Sildenafil (Viagra). Available from: [URL_Link]
- Viagra (Sildenafil Citrate) tablets. Choose brand-name Viagra. Available from: [URL_Link]
- What is Viagra? Available from: [URL_Link]
- How Viagra works. Available from: [URL_Link]
- Viagra – Uses, Side Effects, and More. Available from: [URL_Link]
- Erectile dysfunction: Viagra and other oral medications. Available from: [URL_Link]
- What is Viagra? Available from: [URL_Link]
- Hims vs. Roman. Available from: [URL_Link]
- Use of Sildenafil (Viagra) in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease. Available from: [URL_Link]
- Sildenafil. Available from: [URL_Link]
- Viagra. European Medicines Agency. Available from: [URL_Link]
- How long does viagra take to work? Available from: [URL_Link]
- An Erection That Won’t Quit?! 3 Viagra Myths Debunked. Available from: [URL_Link]
- Taking Viagra for the First Time? Here’s How to Get the Best Results. Available from: [URL_Link]
Viagra helps men get and maintain erections. Take it on an empty stomach at least an hour before sexual activity. Over-4-hour erections might cause irreversible harm.
Cialis and Levitra are other ED drugs like Viagra.